Mengnan

|
- Professional Title:Lecturer
Discipline:Materials Science
Degree:博士
School/Department:卓越工程师学院
E-Mail:
 Contact Information
Contact Information
- ZipCode:
- Fax:
- PostalAddress:
- OfficePhone:
- Email:
- Paper Publications
Construct Stable Charge Carrier Transport Interface for High-Energy-Density Electrodes by Grafting Ion-Conducting Group to Carbon Nanotube Additives
Release time:2025-07-01 Hits:
- Impact Factor:12.1
- DOI number:10.1002/smll.202503375
- Journal:Small
- Key Words:carbon nanotubes, additives, grafting, interphase, energy density, lithium-ion batteries
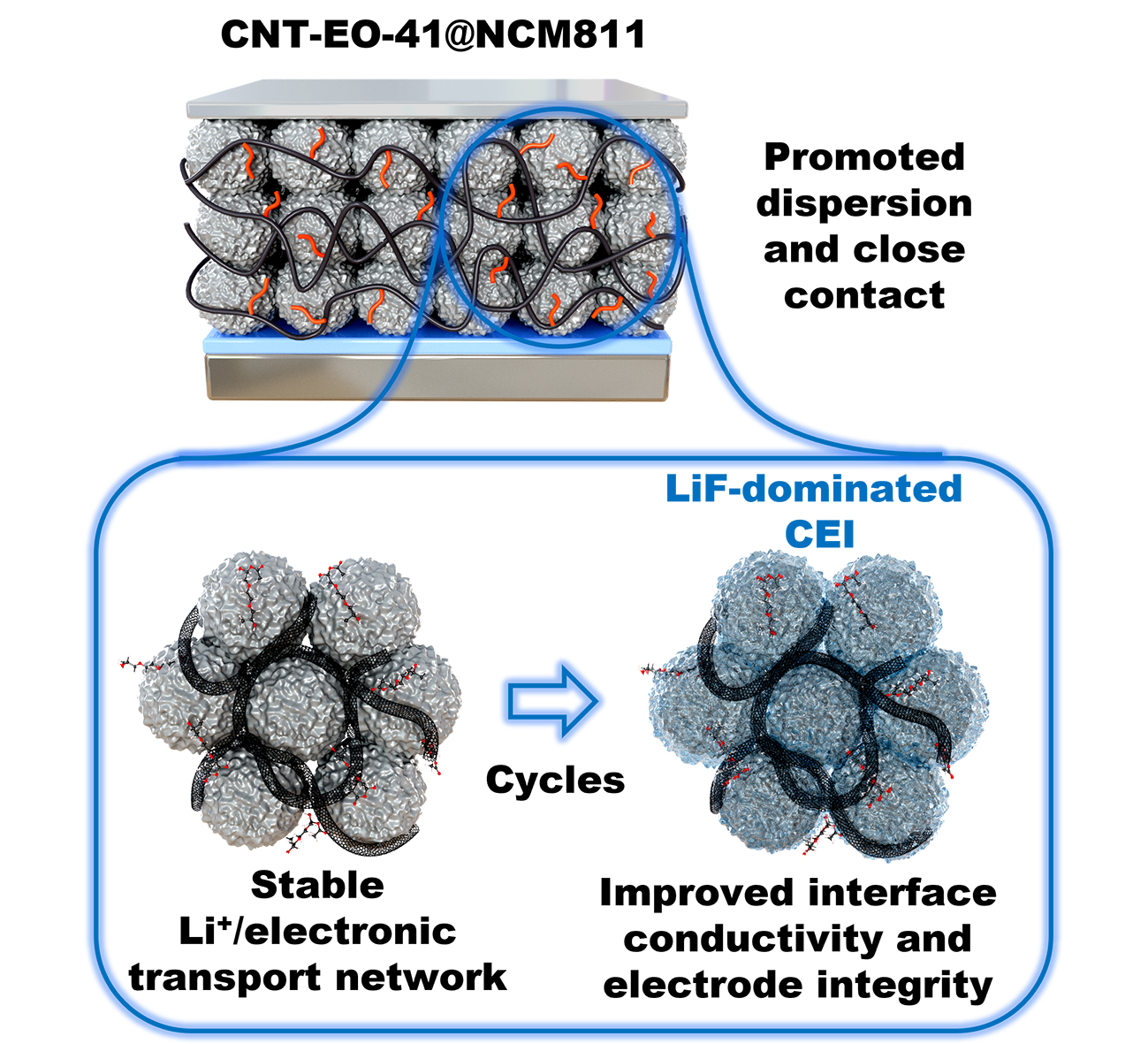
- Abstract:Carbon materials are the key additives for electronic conductivity in electrodes, which determine the electrochemical performances and durability of batteries. Herein, a strategy for grafting ion-conducting groups to multi-wall carbon nanotubes (MWCNTs) is proposed via in situ polymerization induced by a Lewis acid agent BF3, which is generated from the disproportionation of LiBC2O4F2 (LiODFB). The as-obtained MWCNTs demonstrate a narrower particle size distribution in the solution due to the reduced surface defects and steric effect between the grafted oxyethylene (EO) segments. Moreover, the MWCNTs with ion-conducting groups (CNT-EO) show not only good electronic/ionic dual conductivity but also high chemical- and electrochemical- stability up to 4.8 V with the LiNi0.8Co0.1Mn0.1O2 (NCM811) electrode. The CNT-EO integrates the cathode into a monolithic structure through an interconnected 3D dual conductive network, which accelerates the construction of a robust LiF-dominated interphase layer on NCM811. Therefore, the Li/NCM811 cells with CNT-EO additive deliver a high discharge capacity of 183.5 mAh g−1 at 0.5 C, and a significantly improved cycle life of 400 cycles. The strategy of grafting special functional groups to the CNTs is beneficial to construct a stable charge carrier transport interface for electrodes with high-energy density, long life, and high safety.
- Indexed by:Journal paper
- Document Code:2503375
- Discipline:Engineering
- Document Type:J
- Volume:21
- Issue:25
- Translation or Not:no
- Date of Publication:2025-05-12
- Included Journals:SCI